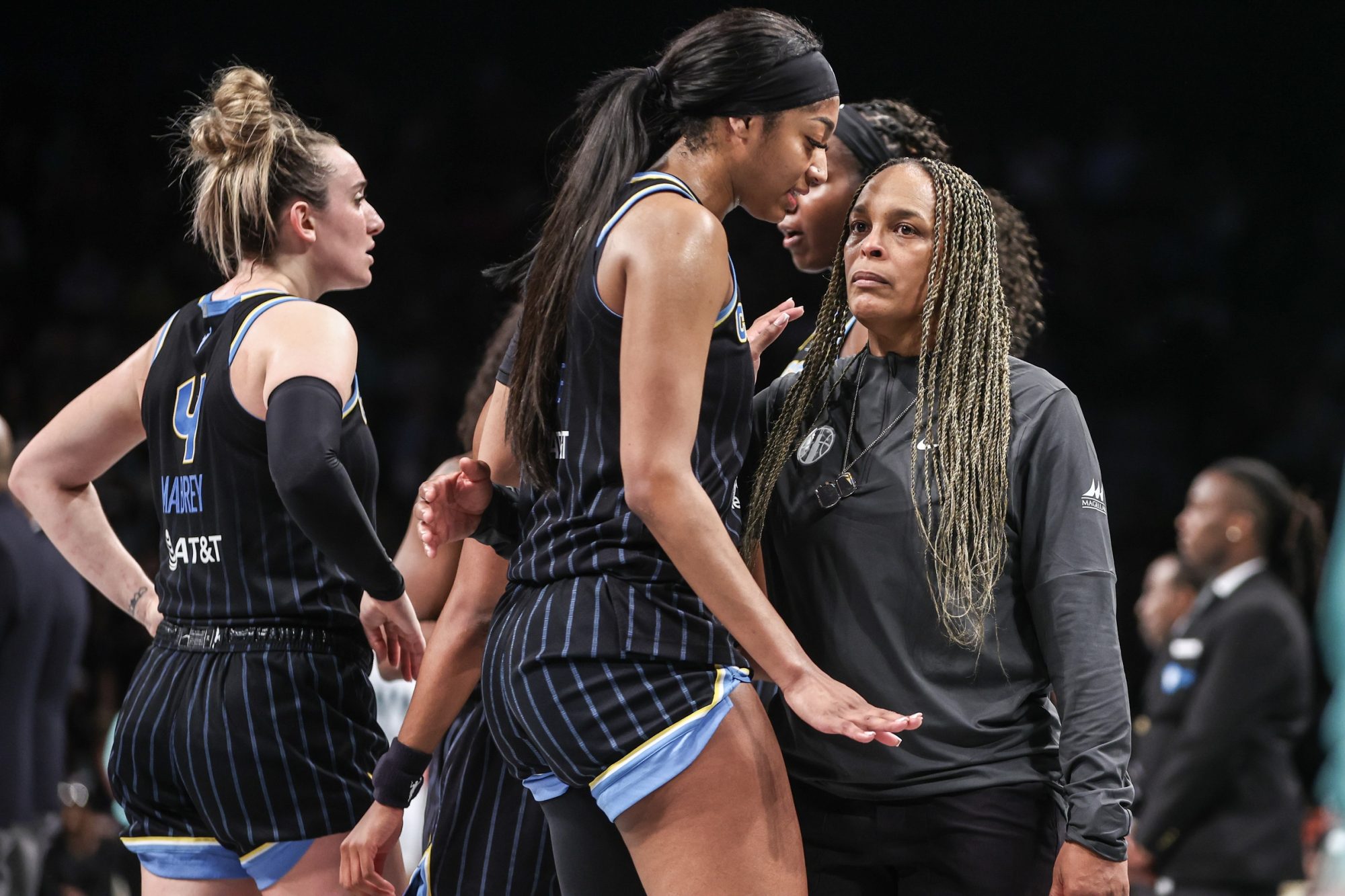
When the Chicago Sky hired Teresa Weatherspoon as head coach last October, it was the beginning of a new chapter. The Hall of Famer was ostensibly replacing James Wade, who led the Sky to a title in 2021 and was one of the final remnants of the championship core.
But last month, the Sky fired Weatherspoon, less than 12 months after she joined the organization. The move shocked the WNBA—including Sky star Angel Reese—but, alongside the firing of Los Angeles Sparks coach Curt Miller three days earlier, it was just the beginning of a massive coaching shake-up across the league.
Five additional head coaches have been let go over the last month, capped off Sunday by the Indiana Fever firing Christie Sides and Monday when the Connecticut Sun parted ways with Stephanie White, who will reportedly return to the Fever. There are seven head coaching vacancies across the WNBA—the Sparks, Sky, Atlanta Dream, Dallas Wings, Washington Mystics, Fever, and Sun—or more than half the league without counting the expansion Golden State Valkyries.
There have also been four GM changes. The Las Vegas Aces and Washington Mystics moved on from championship-winning executives, the Wings announced in October they are in search of a GM, while the Indiana Fever’s Lin Dunn shifted to a senior advisor role to make way for former Wings COO Amber Cox.
While it’s not uncommon for losing teams to let go of head coaches—and six of the seven vacancies are from teams that finished with a .500 or worse record last season—the volume of firings is an anomaly. The question is: Why are so many WNBA teams firing their head coach now?
Incoming Funds
The delta between the budgets of WNBA teams is noticeable. Organizations like the New York Liberty have billionaire owners willing to make splashy investments, while others are scraping for funding.
However, the new media-rights deal coming in 2026—a $2.2 billion deal that could end up more than four times the size of the last deal—will bring an influx of cash to all teams. There are also expansion fees from three new franchises, and likely a fourth, to add to the pot.
With more money flowing in, teams can now throw bigger contracts at names across professional and collegiate basketball. Last season, only two coaches made at least $1 million per year: the Phoenix Mercury’s Nate Tibbetts ($1.2 million) and the Aces’ Becky Hammon ($1 million). The rest of the coaches made $700,000 per year or less.
A seven-figure salary could attract coaches with high-level collegiate or NBA experience (though Weatherspoon was an assistant with the Pelicans before coaching the Sky). A new WNBA head-coaching market could have salaries that mirror, or even exceed, NBA assistant coach salaries. The NBA’s Suns, who have the same owner as the Mercury, paid more than $2 million annually to Kevin Young, the highest for an assistant coach, before he left to coach BYU.
Front Office Changes
A common trend in sports is that new front offices like to hire their own head coach—and not just inherit the one from a previous tenure. Team presidents or GMs can go through the vetting process for potential coaches and be sure that whoever is at the helm is aligned with their vision for the organization.
The Sky are a prime example. Wade played the role of GM and head coach, so both roles were vacant when he left to be an assistant coach for the NBA’s Raptors last July. The Sky ended up hiring Weatherspoon weeks before they announced Jeff Pagliocca as GM.
The same can be said for the Fever, whose new team president, Kelly Krauskopf, and Cox were both hired within the last five weeks before the firing of Sides.






![[Subscription Customers Only] Jun 15, 2025; Seattle, Washington, USA; Botafogo owner John Textor inside the stadium before the match during a group stage match of the 2025 FIFA Club World Cup at Lumen Field.](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/USATSI_26465842_168416386_lowres-scaled.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)
![[Subscription Customers Only] Jul 13, 2025; East Rutherford, New Jersey, USA; Chelsea FC midfielder Cole Palmer (10) celebrates winning the final of the 2025 FIFA Club World Cup at MetLife Stadium](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/USATSI_26636703-scaled-e1770932227605.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)





![[US, Mexico & Canada customers only] Feb 6, 2026; Riyadh, SAUDI ARABIA; Jon Rahm in action during the third round of play at LIV Golf Riyadh at the Riyadh Golf Club.](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/USATSI_28173562_168416386_lowres-scaled.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)

![[US, Mexico & Canada customers only] Sep 28, 2025; Bethpage, New York, USA; Team USA's Bryson DeChambeau reacts after hitting his approach on the 15th hole during the singles on the final day of competition for the Ryder Cup at Bethpage Black.](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/USATSI_27197957_168416386_lowres-scaled.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)
