Fifteen years ago, lawyers representing major U.S. pro sports and the NCAA were engaged in a legal fight over Delaware’s bid to expand sports betting in the state.
They laid out this warning: “Sports lotteries involving single-game betting threaten the integrity of professional and amateur sports and are fundamentally at odds with the principle … that the outcomes of professional and collegiate athletic contests must be perceived by the public as being determined solely on the basis of honest athletic competition.”
The leagues and NCAA prevailed in the case as Delaware was kept from allowing single-game betting. But the decision became moot, in May 2018, when the U.S. Supreme Court struck down the Professional and Amateur Sports Protection Act (PASPA).
Six years and billions of dollars in revenue later, a major moment of reckoning has arrived, and there are signs that the floodgates could open. It’s not just that the legal gambling industry is a behemoth and its marriage to pro leagues is only getting stronger. But the integrity concerns from 15 years ago have been thrust into the spotlight—made more prominent by a confluence of regulation technology and mobile betting, demand for the illegal market, and a slew of nuanced rules for players. This week’s scandals are only the beginning.
“Despite all the efforts, it’s bound to happen,” says longtime SuperBook at Westgate executive Jay Kornegay. “Legalized sports betting is in its infant stages. There’s a lot of naive people who believe they can circumvent policies. Operators have a vested interest in keeping these games true and fair. Integrity is our product. We don’t want to accept wagers on something that’s predetermined.”
Since PASPA’s repeal, the known violations have largely been limited to violation of league rules—like the several NFL players suspended for placing non-NFL bets on mobile betting apps within team facilities.
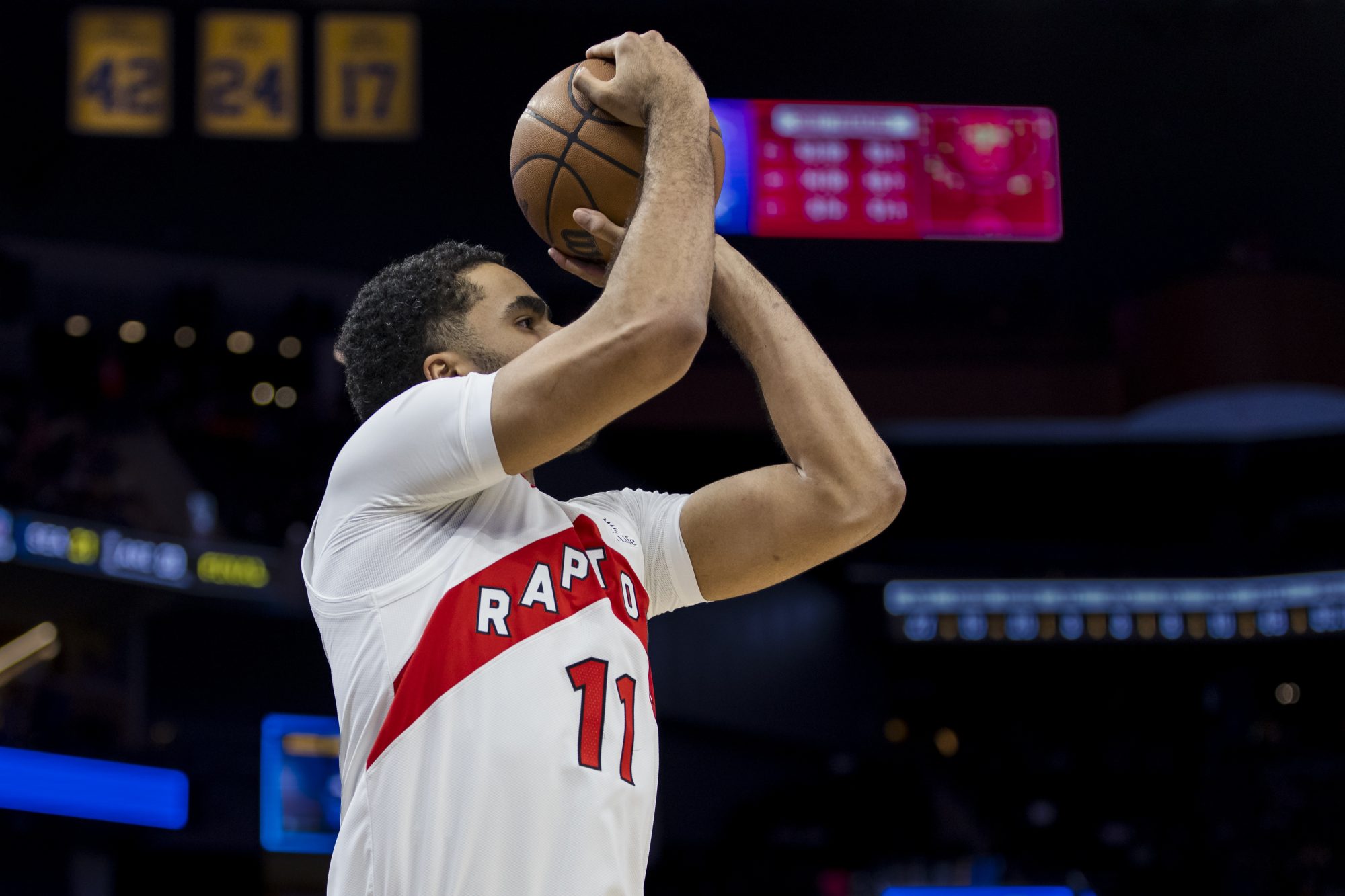
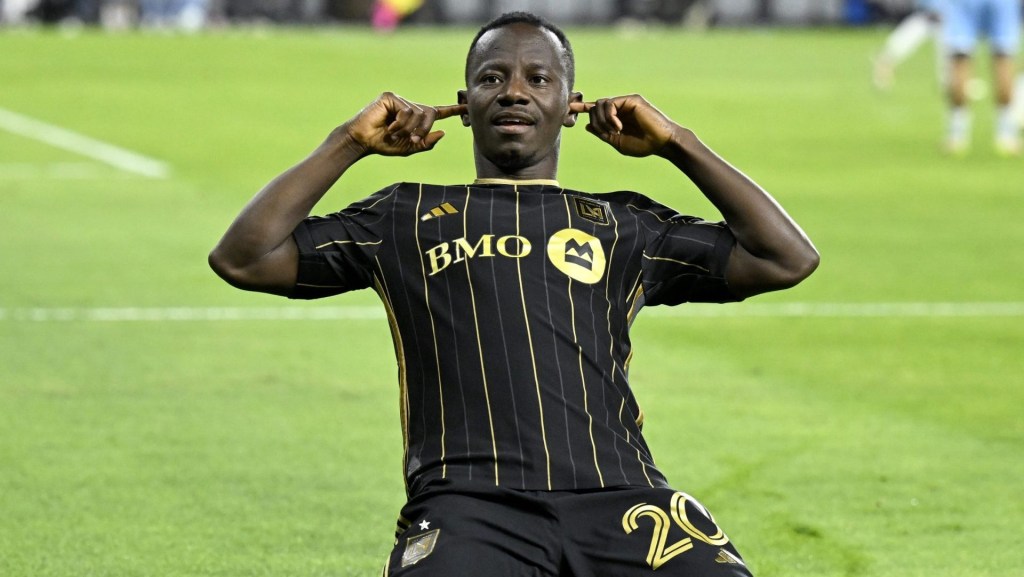
But this past week, three major betting scandals came to a head: San Diego Padres infielder Tucupita Marcano was banned for life by MLB for betting on baseball, and four others players were suspended; Ippei Mizuhara, the former interpreter and confidante of Shohei Ohtani who illegally wagered millions pilfered from the Los Angeles Dodgers star (sports betting is illegal in California), pleaded guilty; and an illegal bookie tied to banned former Toronto Raptors player Jontay Porter (above) was arrested by federal authorities.
“Banning a player for life sends a strong message,” famed sports agent Leigh Steinberg says. “[Marcano] may not be Shohei Ohtani. He’s not the best player in baseball, but still banning someone for life presents a stop sign. There’s a deterrent effect.”
Mizuhara, who stole nearly $17 million from Ohtani and compiled more than $40 million in gambling losses, faces up to 33 years in federal prison after his guilty plea Tuesday. Later Tuesday, the MLB said in a statement that the federal investigation of Mizuhara revealed “Shohei Ohtani a victim of fraud,” which Ohtani insisted when the news broke earlier this year.
“I think we dodged a bullet with [Mizuhara],” says Ken Adams, a senior analyst at CDC Gaming Reports. “If that had been Ohtani making the bets, and not his interpreter, it would have blown up to become a national scandal.”
In April, Porter was banned for life by the NBA after a league investigation revealed he passed along injury information to gamblers and exited games early to pay off gambling debts. The bookie who allegedly placed prop bets fueled by Porter’s insider information was arrested Monday by federal authorities at John F. Kennedy International Airport as he attempted to board a flight to Australia.
“The danger has exponentially increased by the presence of new prop bets,” says Steinberg. “There are so many new ways athletes can get sucked into betting.”
According to Steinberg, it’s also possible that inside information is not confined to each league and its respective athletes: “So, you can’t bet on your own sport, but it’s not like football players don’t know basketball players. They can share inside information because athletes are part of a large fraternity.”
Thirty-eight states and D.C. offer some form of legalized sports betting. Revenues generated from state-sanctioned sports betting—which didn’t exist outside of Nevada until PASPA’s repeal—have climbed from $135 million in 2017 to $10.9 billion last year, according to the American Gaming Association.
Much of the betting industry’s growth—and misconduct—has been fueled by mobile betting, which is available in 30 states plus D.C.
“The Supreme Court didn’t anticipate [the explosion of mobile betting],” says Adams. “Without mobile betting, a lot of these violations would be non-issues.”
Mobile betting operators are mandated to ensure a bet placed by a customer who claims to be in a state with legalized sports betting was made in that state—and by the person who owns the account.
“With more regulated betting, more of these cases are coming to the surface through detection and investigations [by sportsbooks],” says Dan Wallach, sports and betting law attorney. “The mistake that so many of the professional athletes are making raises concerns that are not getting the message.”
Companies like GeoComply and Radar seek to ensure users aren’t spoofing their location, something that some involved athletes at the University of Iowa and Iowa State were accused of doing last year.
“We can be super accurate, even indoors,” says Nick Patrick, CEO and cofounder of Radar. “You want to make sure to get the location data as accurate as possible. You also want to be able to trust it. You want to make sure it’s not spoofed or tampered with.”
The slow drip of gambling violations shows no signs of halting.
“Are there going to be scandals down the road? Most likely,” says Kornegay.
For many fans, and bettors, the most important concern for the future of sports remains. The concern over integrity is no different than it was in 1919 after the Black Sox threw the World Series, or 15 years ago when lawyers raised it in the fight over Delaware sports betting.
“Bad behavior by athletes doesn’t kill professional sports. There’s been plenty of that,” says Steinberg. “The only thing that could [hamper the popularity of sports] is the perception by fans that they were watching [professional] wrestling. That it is somehow scripted or predetermined or there were actions or facts going on the public wasn’t aware of, and we have seen that happen.”