One of the biggest pioneers for equal pay in global soccer — and equitable treatment for female athletes — will return to the global stage for the first time since 2015.
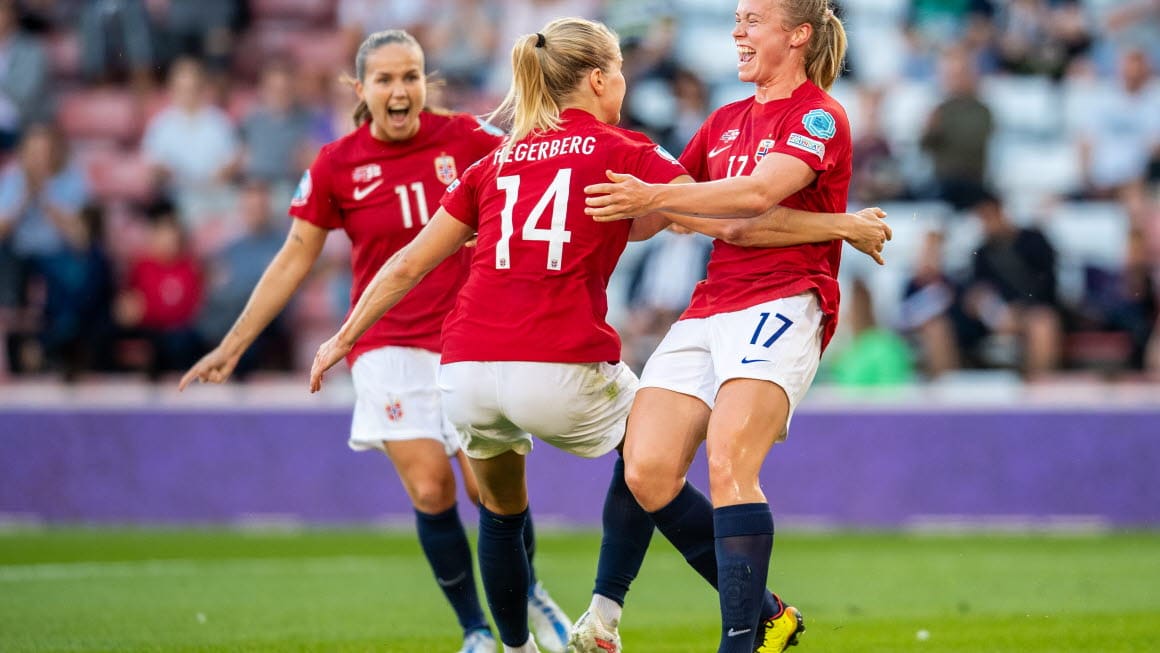
Norwegian star Ada Hegerberg will represent her nation in the 2023 Women’s World Cup’s inaugural group-stage match against New Zealand on Thursday morning.
The U.S. team receives most of the attention for its equal pay fight, but Hegerberg almost single-handedly forced the Norwegian Football Association (NFF) to become the first national soccer governing body in the world to agree to equal pay — five years before U.S. Soccer inked its own agreement.
For years, the 28-year-old reportedly tried behind the scenes to improve equity between the men’s and women’s teams. In the summer of 2017, she launched a protest against unequal treatment of players at the hands of the NFF, refusing to don the Norwegian kit and playing only for her club team, French side Lyon.
Unlike the players who stood in lockstep to fight U.S. Soccer for equal pay, Hegerberg was the sole protestor on the team. The NFF itself released statements against her, saying that she had blindsided the team — accusations she disputed in a 2020 ESPN article.
“I was very alone in my decision, back in 2017, and that’s not something I say out of pity for myself; it’s just the way it was back then,” Hegerberg said upon arriving at this year’s World Cup.
Eventually, the federation backed down. In October 2017, the NFF announced it would agree to pay both its men’s and women’s players equally. Perhaps a blueprint for the U.S. contract, the Norwegian men’s team agreed to relinquish some of its earnings to help fund women’s salaries — a necessity given that FIFA doesn’t offer equal prize money for the men’s and women’s World Cups. The agreement was signed that December.
“It is very positive that Norway is a pioneer,” NFF Secretary General Pal Bjerketvedt said then. “At the same time, this is a recognition for women’s football in general, and it’s amazing to see how much this means to the players and what enormous attention the issue has gained internationally.”
But Hegerberg wasn’t satisfied. When she originally left the Norwegian team, she gave the federation a list of demands that went far beyond equal pay, covering everything from practice facilities and trainers to equipment. Those demands didn’t appear to be met, so Hegerberg decided to sit out the 2019 World Cup. The team made it to the quarterfinals, but certainly could have used Hegerberg — by then a global soccer star.
“We’re not even talking about equal pay here,” Hegerberg said. “We’re talking about minimum conditions in order to feel that you’re being taken seriously and so you can actually perform at the level you want and need to be at.”
Her decision was a major personal sacrifice given that she was at the top of her game — just a year earlier, she had become the first women’s player to win the prestigious Ballon d’Or. But for Hegerberg, it was about more than football. After all, even her acceptance of the award was interrupted by blatant misogyny.
Even amid the U.S. equal pay fight, and as other teams began to speak up about equity, Hegerberg’s protest was controversial. One U.S. national team member reportedly criticized Hegerberg’s decision to sit out, saying her demands for a post-equal pay contract weren’t “specific” enough.
But that didn’t stop Hegerberg from standing up for better treatment. She reenters the World Cup as one of the biggest advocates for equity in women’s soccer across the globe.
“I don’t think things will change without women standing up,” Hegerberg said.