Soccer’s Champions League is back—with an elevated prize pool, an expanded competitive format, and also no shortage of player unrest.
The UEFA-organized competition involving Europe’s top pro clubs began Tuesday, featuring a $2.71 billion prize pool, increased from a prior $2.2 billion. A revamped and expanded group stage—now known as the “league phase”—organizes the 36-team field in a single group before moving to knockout rounds. The new structure will feature four additional competing teams and 64 additional matches over the course of the tournament.
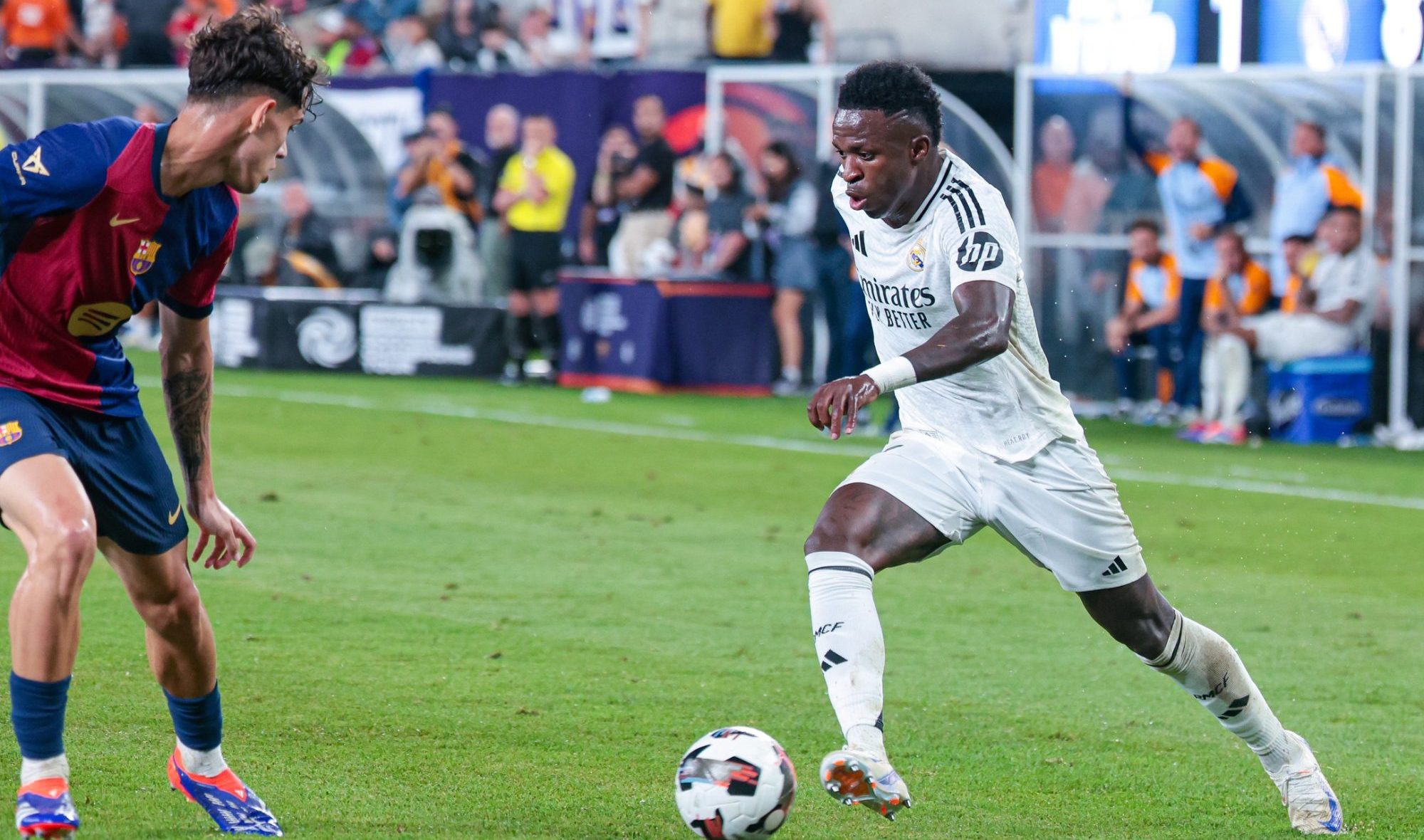
Real Madrid will seek to defend its title, won less than four months ago. Premier League power Manchester City, meanwhile, is the betting favorite, even as it faces allegations of financial misconduct back home.
As action on the pitches begins, though, a growing number of players are questioning the wisdom of expanding this event along with a still-robust domestic club schedule, a new, 32-team Club World Cup organized by FIFA, international friendlies, and a men’s World Cup that will grow to 48 teams in 2026.
Because of that, a players’ strike—something that is much more of a rarity in European sports than in North America—is increasingly possible.
“I think we are close to that,” Manchester City star midfielder Rodri said Tuesday. “It is easy to understand. If you ask any player that, he will say the same. It is not the opinion of [just] Rodri or whoever. It’s the general opinion of players. And if it keeps this way, there will be a moment when we have no other option, I really think. It’s something that worries us because we are the guys that suffer.”
Individual players and FIFPRO, the global soccer players’ union, have been sounding similar alarms for months over the sport’s increasingly compressed schedule. In June, French superstar Kylian Mbappé, now playing professionally for Real Madrid, said European soccer is “getting closer to the NBA model,” with seasons of 70 games—to the detriment of the sport.
Now, with UEFA’s showcase event unfolding, many of those same players and organizations are shining a new spotlight on the issue.
“We understand that we have the side of the media and TV, we have the side from UEFA, from FIFA, from the Premier League, and the other domestic competitions,” said Liverpool goalkeeper Alisson Becker. “We are not stupid. We understand that people want more games. But the reasonable thing would be for all these sides that I mention and the people who are responsible for making the calendar to sit together and to listen to all the parts, including the players.”
Big Workload
High-performing teams such as Manchester City are firmly in line to play more than 60 matches per year. That figure is well above an optimal level in the minds of some players, such as Rodri, who point to diminishing returns from players after about 40 games played annually.
“Not everything is money or marketing. It is also the quality of the show,” Rodri said. “In my opinion, when I rest, when I’m not tired, I perform better. If people want to see better football, we need to rest.”