The NBA is “tripling down” on its investment in girls’ basketball as part of efforts to grow the youth game amid an uptick in broadcast viewership at the college and WNBA levels.
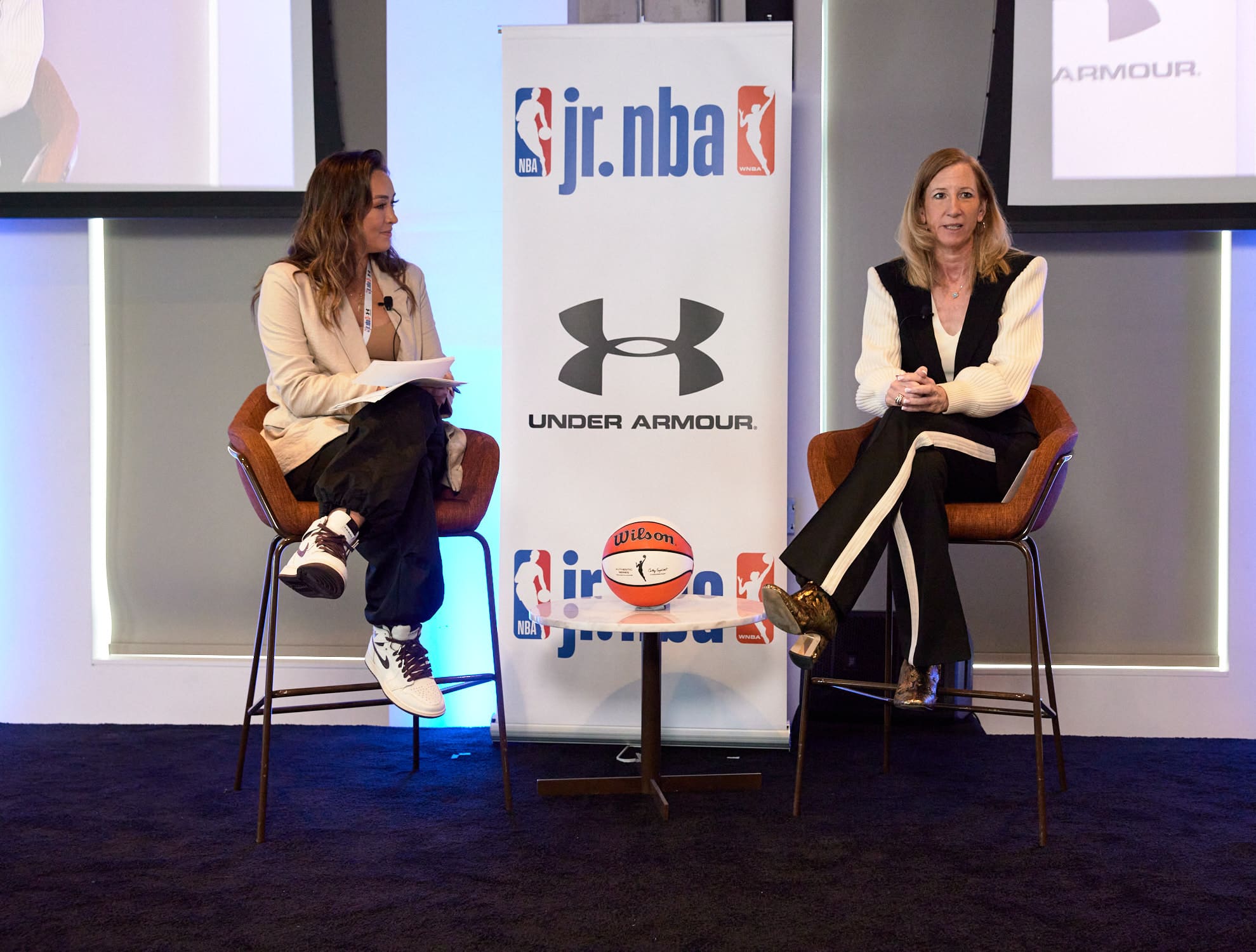
“We are doubling and tripling down on our investment in girls’ basketball. We see that as a huge priority from an equity perspective and continuing to grow the game perspective for both our NBA and WNBA business,” David Krichavsky, NBA SVP and Head of Youth Basketball Development, told FOS Wednesday at the Jr. NBA Conference in New York City.
Krichavsky oversees U.S. operations for the Jr. NBA, the league’s youth basketball program with events that reach more than 40 million youth across 160 countries. Last summer, the NBA and WNBA launched Jr. NBA Leagues, a network of youth basketball leagues for girls and boys ages 6-14 in cities across the U.S.
ESPN’s broadcast of the 2023 WNBA Draft was the league’s most-watched in 19 years. LSU’s NCAA championship win over Iowa on ESPN averaged 9.9 million viewers, making it the most watched women’s college basketball game on record. BetMGM also reported a 30% year-over-year increase in betting handle for this year’s women’s college basketball tournament.
“The momentum that exists in women’s basketball at the WNBA level and the NCAA level, with the record viewership and engagement they had around this year’s NCAA tournament, is absolutely trickling down to the youth level,” Krichavsky said. “We are very much trying to seize that momentum to grow girls’ participation. Women’s basketball is surging, and we’re working hard to capitalize on that momentum.”
Kids in Jr. NBA Leagues play in licensed jerseys from NBA and WNBA teams, and participation is expected to reach 500,000 per year by 2027. The Jr. NBA also operates Her Time to Play, a free curriculum for girls that pairs on-court training with off-court life skills and aims to increase coaching opportunities for women in youth sports.
More than 28 million people ages six and over in the U.S. played basketball at least once in 2022, ranking as the country’s most popular team sport and youth sport. Jr. The 40 million kids in Jr. NBA programs is down from its peak 60 million kids served before the pandemic, which is why Jr. NBA Leagues was launched.
“The pandemic took trends and accelerated them. As it relates to the professionalization of youth sports, it was the travel programs that continued to thrive in the pandemic that bounced back right away. Recreational play shut down and didn’t come back as strong, which is why a program like Jr. NBA Leagues is so essential,” Krichavsky said. “It’s designed to elevate recreational community-based play, working with a network of national partners like Boys and Girls Clubs,YMCAs—community-based organizations that may not require you to travel around the country to play or pay huge fees.”















![[US, Mexico & Canada customers only] April 13, 2025; Sakhir, BAHRAIN; Oscar Piastri leads George Russell into the first corner at the start of the race during the F1 Bahrain Grand Prix at the Bahrain International Circuit.](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/USATSI_25925940_168416386_lowres-scaled.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)
