The coronavirus pandemic has upended the sports industry with many teams’ bottom lines hit hard with European soccer clubs not being an exception.
As fans were told to stay home, ticket sales — a lucrative source of revenue — came to a grinding halt.
But those clubs have found new fans as of late that could help buoy their finances: private equity firms.
Italy’s Serie A has been hit hard due to months worth of canceled and postponed matches. The league’s revenue is projected to be $2.4 billion, dropping from $2.9 billion last year, according to a forecast by analysts at Deloitte.
As the league suffers, private equity investors like CVC Capital Partners, Bain Capital and Cinven are circling the league for a possible stake in its broadcast rights operation. And if a deal goes through, then the arrival of new capital will significantly help the league and its teams struggling due to the pandemic.
Italian soccer club AS Roma, the home of the now retired Francesco Totti, was bought by Texas-based billionaire Daniel Freidkin for almost $700 million in August. The Iowa-based Krause Group bought a controlling stake of Parma Calcio for $100 million in September in a bid to restore one of Serie A’s most storied clubs.
Along with that, A.C. Milan has been run by the private equity group Elliott Management since 2018 after Li Yonghong, the club’s previous owner, defaulted on a loan to the company. Billionaire Rocco Commisso also acquired ACF Fiorentina for an undisclosed sum in June 2019.
Serie A has become a breeding ground for private equity firms as media rights have grown in the league along with the potential to build on undervalued digital assets. At the same time, outside investments have provided the much needed cash for the clubs to stay afloat.
“The trend will accelerate in 12 to 24 months in European soccer,” said Clive Reeves, PwC senior sports business advisory manager. “Private equity will be an option for current football owners to weather the storm.”
Along with the Italian league, France’s Ligue 1 has also seen an influx of private equity. In July, New York City-based RedBird Capital Partners bought an 85% stake in Toulouse FC. Girondins de Bordeaux, another French club, was sold to Miami-based General American Capital Partners in 2018.
The increase of U.S. private equity investment in the Italian and French leagues reveal how lucrative it is for clubs with strong local brands to be opened to the international market. And private equity firms provide the operational expertise — the how — for the clubs to not only diversify their revenue streams, but also build different individual brands from their assets, according to Reeves.
“I think it will be beneficial and help football evolve,” Reeves added.
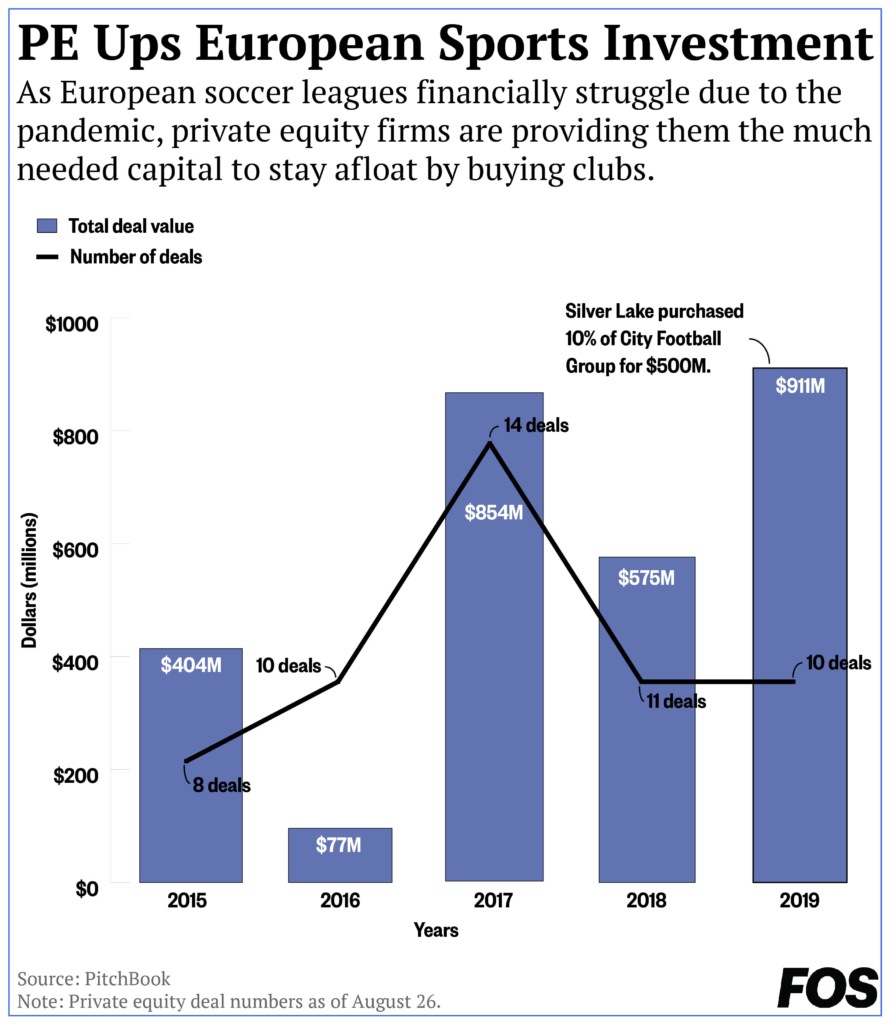
England’s Premier League is also facing the same crisis, as it expects to see revenue drop from $6.9 billion to $5.7 billion, providing further opportunity for private equity. In 2019, Silver Lake acquired a minority 10% stake for $500 million in City Football Group — Manchester City’s holding company.
With the continued proliferation of U.S. private equity firms on the continent, the struggling European soccer clubs could see themselves grow into different types of businesses while creating a synergy of soccer clubs throughout Europe.
“The entry of a private investor will make a true difference only if it enables a ‘new way of working’ — access to fresh talent and strategic thinking that would have been impossible to incubate in the context of a traditional rights owner and its structures,” said Christian Müller, senior vice president, Infront Sports & Media.







![[Subscription Customers Only] Jun 15, 2025; Seattle, Washington, USA; Botafogo owner John Textor inside the stadium before the match during a group stage match of the 2025 FIFA Club World Cup at Lumen Field.](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/USATSI_26465842_168416386_lowres-scaled.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)
![[Subscription Customers Only] Jul 13, 2025; East Rutherford, New Jersey, USA; Chelsea FC midfielder Cole Palmer (10) celebrates winning the final of the 2025 FIFA Club World Cup at MetLife Stadium](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/USATSI_26636703-scaled-e1770932227605.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)







