Call it the Queen Anne Gambit.
Kalshi, Robinhood, and others have been hit with five new lawsuits in five different state courts over allegations that their sports event contracts are in fact illegal sports betting products disguised as financial products. The nearly identical lawsuits each cite versions of the Statute of Anne, a centuries-old provision that voids certain gambling debts and allows third parties to sue for damages if the original bettor fails to act within six months.
The five suits were all filed last week, in state courts in Kentucky, Illinois, Massachusetts, Ohio, and South Carolina. The plaintiffs are all newly formed limited liability companies with uniform names—Kentucky Gambling Recovery LLC, Illinois Gambling Recovery LLC, and so on. Each LLC was incorporated in Delaware on March 18. No additional information about them was immediately available.
All of the suits are seeking damages in the amount of total losses incurred by users, and they want that figure to be dated up to the day a final judgment is made. Three of the suits (Kentucky, Illinois, Massachusetts) want those damages tripled. One (South Carolina) wants the damages quadrupled. The suit in Ohio simply seeks damages in the amount of total losses.
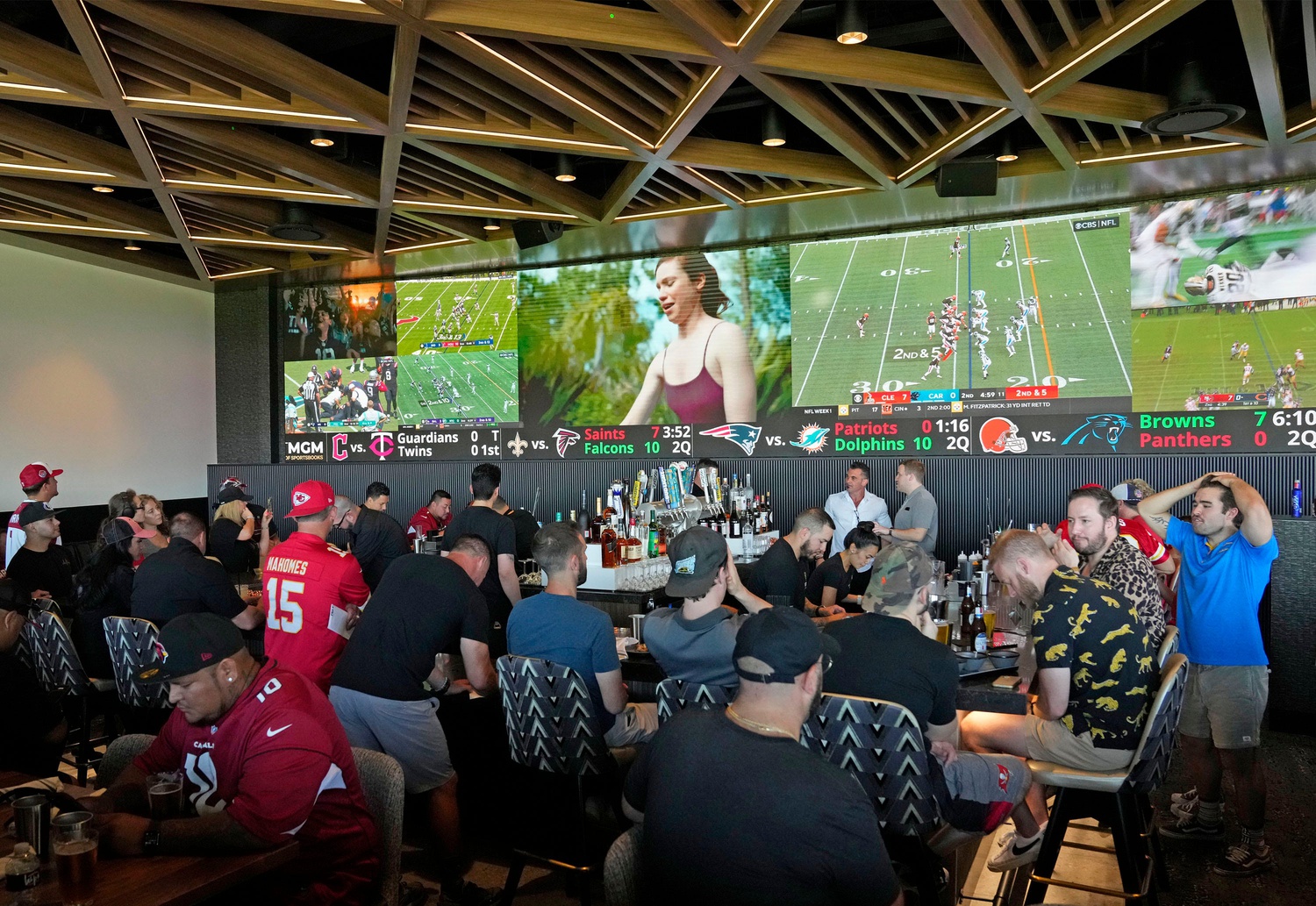
Drama over the sports “prediction” space is nothing new. Kalshi, Robinhood, and others have been battling in court and with state regulators since a high-profile Kalshi victory in the D.C. Circuit last year over the legality of its offerings, allowing users to trade on the outcome of political events like the U.S. presidential election. In the aftermath of that case, Kalshi launched sports event contract offerings in January, and Robinhood and Kalshi entered into a high-profile partnership. Since the debut of the sports offerings, more than $1.6 billion has been traded across 5.2 million trades, according to Kalshi.
To date, at least seven states have issued cease-and-desist orders to Kalshi and others (including Robinhood and Crypto.com)—Nevada, New Jersey, Illinois, Maryland, Ohio, Montana, and Arizona. Kalshi has been aggressive in its response, filing federal lawsuits against regulators in Nevada, New Jersey, and Maryland. It has scored significant early victories in the Nevada and New Jersey suits, although those cases remain ongoing.
These sports event contracts are controversial because they appear so similar to sports betting, and detractors assert the providers are skirting federal law by enabling what they claim is sports betting in all 50 states. Kalshi has argued there is a key distinction: Traditional wagers see users betting against “the house”—casinos or sportsbooks that set the odds and profit when bettors lose—while sports prediction markets offer nationwide marketplaces where users trade against one another.
18th-Century British Law
The new suits all cite versions of the Statute of Anne, a British law passed under Queen Anne in 1710. Many modern U.S. states have adapted that statute into their own laws. The lawsuits each state that, “lured by the potential riches of an untapped market, a group of companies has taken to offering illegal, unregulated gambling products” to residents.
“While masquerading as novel securities offerings, these event contracts are in truth nothing more than illegal, unregulated wagers on the occurrence (or non-occurrence) of specific future events,” the suits say.
In court, Kalshi has contended that its sports event contracts are legal because they fall under the “exclusive” jurisdiction of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), a federal regulator that oversees commodities like grains and oil, but also sports when considered in a trading context.
A Robinhood spokesperson issued a statement to Front Office Sports on Monday saying its event contracts “are regulated by the CFTC and offered through Robinhood Derivatives, LLC, a CFTC-registered entity, allowing retail customers to access prediction markets in a safe, compliant, and regulated manner.”
“So far, two federal courts have made initial rulings that the CFTC’s rules preempt state law and we intend to defend ourselves against these claims,” the statement said, nodding to Kalshi’s early wins in Nevada and New Jersey.
A notable escalation has emerged from the new suits. In addition to Kalshi and Robinhood, the list of defendants includes Susquehanna International Group and Webull Corporation, both of which are involved with prediction markets but not as directly. Susquehanna, a quantitative trading firm, is accused of helping provide liquidity for the event contracts, while Webull, a stock trading platform, is accused of helping facilitate the so-called “trades.”
Kalshi declined to comment. Attorneys who filed the lawsuits did not immediately respond to requests for comment, nor did Susquehanna or Webull.
The legal battle comes amid a backdrop of rising interest in the sports prediction space. FOS reported last week that FanDuel and Kalshi have held discussions about a deal of some kind that would include various betting efficiencies. Industry sources say nearly all the sportsbooks and federally regulated exchanges (which include a number of other crypto exchanges that don’t currently offer prediction markets) are having discussions with each other to figure out frameworks of potential collaborations.
Top executives for most of the top sports betting players—including FanDuel, DraftKings, Penn Entertainment, and BetMGM—have made recent comments about the burgeoning market. The interest makes sense; places like Kalshi operate in all 50 states, while sports betting is legal in only 39.





![[Subscription Customers Only] Jul 13, 2025; East Rutherford, New Jersey, USA; Chelsea FC midfielder Cole Palmer (10) celebrates winning the final of the 2025 FIFA Club World Cup at MetLife Stadium](https://frontofficesports.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/USATSI_26636703-scaled-e1770932227605.jpg?quality=100&w=1024)